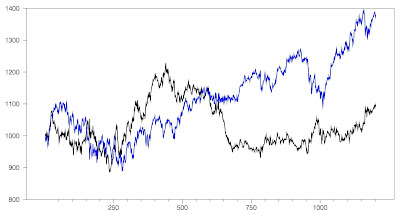
Cambria Funds have launched a new managed futures ETF – MFUT – managed by Chesapeake - Jerry Parker's (one of the turtle traders) firm. I compared the historic performance of the Chesapeake Diversified Plus managed futures program to the Winton Global Alpha Fund since 1996:
Clearly, Winton has outperformed Chesapeake and with substantially less volatility. The average return of Chesapeake has been 11.6% p.a., while Winton achieved 15.0%. Chesapeake's information ratio (Sharpe ratio with a zero percent hurdle) was only 0.44, while Winton's was 0.96.
It seems that Chesapeake's volatility decreased after about 2012. So let's focus on the period since then. Since the beginning of 2012 Chesapeake has outperformed Winton with an average annual return of 8.8% vs. 7.3%. However, Winton was still less volatile with an information ratio of 0.77 vs. Chesapeake's 0.52.
The full period, the correlation between the monthly returns of the two funds was only 0.44. Since 2012 it was 0.54. So, there it would seem there is a potential diversification case for investing in both funds. However the information ratio of an equal weight combination of the two funds is lower than that of Winton alone. This is true for both the full period and the post 2011 period. So, based on this, I won't be investing in MFUT.