I wanted to understand why spending in the 2018 calendar year was up 28% on 2017. The first step was computing a spending breakdown for the 2017-18 financial year. The period is different and the definitions of income and spending are different than in my usual accounts to make it more comparable with other income and spending breakdowns on the web. I now computed the spending breakdown for the second half of 2018 and we can compare monthly spending in this period to that in 2017-18:
Spending was up by 7.5%. So not as dramatic a growth rate. The biggest difference between the two periods, is that in the first period we spent a lot on travel and in the second on health. In fact, the travel spending was mainly in the second half of 2017-18 - i.e. in the first half of 2018. So, 2018 had high spending because of both travel and health spending being up strongly on 2017. The way I usually compute spending and income is to include any refunds for medical spending as income rather than reducing spending by the amount of the refund, which I am doing here. So, that pushed up spending even more. I'm glad I now understand why our spending increased so much.
Another major change is that cash spending was down in the second half of 2018. That was because I had access to the statement for my Qantas Cash card – only the last 13 months is online. In the previous period, I treated all spending on the card as cash spending.
Going forward, I expect medical expenses to be lower this half year and travel expenses to be much lower than in the first half of 2018. Given that, 2019 calendar year spending might be lower than 2018 spending.
Wednesday, January 30, 2019
Tuesday, January 29, 2019
Gold
Put my toes into the water by buying a small 0.5% position using the IAU ETF. I've posted about gold previously and it is in our long-term allocation to allocate 6% to gold.
Saturday, January 26, 2019
Spending Breakdown
After a discussion with friends at lunch yesterday and some blogposts I read recently, I decided to try to find out what we are spending on. I haven't done this in more than two decades I think. I looked at the 2017-18 financial year so that I can also easily include official income and tax figures in the total. It's all in Australian Dollars of course:
Income is gross income from our tax returns plus employer superannuation contributions which which don't enter taxable income. Income includes salaries and investment income etc.
Next we deduct taxes. As franking credits – tax credits for corporation tax paid by Australian companies are included in taxable income, they need to be deducted as we don't actually get the cash. Then there is 15% tax on superannuation (retirement) contributions. In total tax is 26% of gross income. Next I deduct some financial costs that are deducted from gross income to get to taxable income. There are more of these deductions actually, but some I have included in our spending.
Of the AUD 216k of net income half was spent and half saved.
The big spending items are mortgage interest, supermarkets etc, cash spending, mail order, childcare etc, and travel (flights, accomodation etc). Cash spending includes both spending actual cash and spending using our Qantas cash cards. I haven't gone into the accounts for the latter, though maybe I should. Some of the other spending categories very low compared to the actual amount spent on these because a lot of the spending is in cash. Possibly the most important of these is restaurants. Yes, there is a lot of fuzziness in these numbers because we don't budget and spend a lot in cash.
Am happy to get feedback on how we can save money, though I'm not really into "frugality" for it's own sake. Or maybe you would just like to compare the differences with other posted spending breakdowns.
P.S.
Qantas only provide online statements for the last 13 months. So, I can't now do a breakdown of those accounts for 2017-18. Maybe next year.
Income is gross income from our tax returns plus employer superannuation contributions which which don't enter taxable income. Income includes salaries and investment income etc.
Next we deduct taxes. As franking credits – tax credits for corporation tax paid by Australian companies are included in taxable income, they need to be deducted as we don't actually get the cash. Then there is 15% tax on superannuation (retirement) contributions. In total tax is 26% of gross income. Next I deduct some financial costs that are deducted from gross income to get to taxable income. There are more of these deductions actually, but some I have included in our spending.
Of the AUD 216k of net income half was spent and half saved.
The big spending items are mortgage interest, supermarkets etc, cash spending, mail order, childcare etc, and travel (flights, accomodation etc). Cash spending includes both spending actual cash and spending using our Qantas cash cards. I haven't gone into the accounts for the latter, though maybe I should. Some of the other spending categories very low compared to the actual amount spent on these because a lot of the spending is in cash. Possibly the most important of these is restaurants. Yes, there is a lot of fuzziness in these numbers because we don't budget and spend a lot in cash.
Am happy to get feedback on how we can save money, though I'm not really into "frugality" for it's own sake. Or maybe you would just like to compare the differences with other posted spending breakdowns.
P.S.
Qantas only provide online statements for the last 13 months. So, I can't now do a breakdown of those accounts for 2017-18. Maybe next year.
Friday, January 25, 2019
New Investment: Santander UK
Bought my first US corporate bond - a Santander UK bond maturing on 14 March. This supposedly gives a yield per annum of about 2.85%, which is more than treasuries of the same maturity. The original coupon on the bond is 4.2575%, so it is trading at a price of above 100. It pays quarterly interest. Fees for trading corporate bonds are higher than for treasury bonds at Interactive Brokers, but I still figured it was worth it.
Santander UK is the result of the merger of three former UK "building societies" - a bit like credit unions. It is owned by Spain's Banco Santander group but is managed separately. The maturity date is before the scheduled Brexit date on 29 March, so I figure Brexit shouldn't affect getting paid when the bond matures. The bonds are denominated in US Dollars not Sterling.
Tuesday, January 22, 2019
Interesting Paper from GMO on Bursting Stock Market Bubbles and Anti-Bubbles
Here is the paper. Yes, they think that we were in a bubble in 2017 and much of 2018 and the last quarter of 2018 was the beginning of the bursting of the bubble. The problem with the CAPE measure of valuation they use is that it is so backward-looking. If profits are growing fast, CAPE will be high because it uses the average profits of the last 10 years. It has the built-in assumption that profits growth is very strongly mean-reverting.
Monday, January 21, 2019
Likely Political and Economic Scenario for Australia
A couple of days ago I posted a list of all 12 of Labor's proposed tax increases. How likely is it that these will actually be enacted? Labor is unlikely to gain control of the Senate. So, they will need the support of minor parties and independents to push through their program. A quite likely scenario is that there will be a recession in 2020 and the minor parties will be very resistant to raising taxes in those conditions, especially on housing. Or Labor will decide to postpone some of the proposals in reaction to a recession. Then Labor is likely to not be re-elected in 3 years if unemployment is rising etc. So, at this point I would put even odds on most of this agenda being enacted.
Sunday, January 20, 2019
How Has Yale Done Since the Financial Crisis?
Just following up on Financial Independence's comment on my post linking David Svensen's 2008 lecture. How has Yale done since Svensen's lecture? It is easy to find out by checking the endowment's annual reports. Yale's financial year is from July 1st to June 30th. The graph shows Yale's total return index against the MSCI, S&P 500, and HFRI, where the others are all calculated on a July to June basis too.
Yale has performed quite well, eventually outperforming the MSCI World Index, but underperforming the S&P 500. Yale's diversification didn't help in the financial crisis. Their returns were just as negative as those of the MSCI and the S&P 500 in 2008-9. By contrast, the HFRI suffered only small losses in 2008-9. The bottom line is that Yale's returns are quite similar to an equity index.
Here is their asset allocation over the years:
Prior to 2013 they didn't report venture capital separately from buyout funds and so "Leveraged Buyouts" represents all private equity in the earlier years. Also, prior to 2009 they didn't report real estate and natural resources separately and so "natural resources" covers both. Over the years they have increased private equity and foreign stocks and reduced real estate and domestic stocks.
Yale has performed quite well, eventually outperforming the MSCI World Index, but underperforming the S&P 500. Yale's diversification didn't help in the financial crisis. Their returns were just as negative as those of the MSCI and the S&P 500 in 2008-9. By contrast, the HFRI suffered only small losses in 2008-9. The bottom line is that Yale's returns are quite similar to an equity index.
Here is their asset allocation over the years:
Prior to 2013 they didn't report venture capital separately from buyout funds and so "Leveraged Buyouts" represents all private equity in the earlier years. Also, prior to 2009 they didn't report real estate and natural resources separately and so "natural resources" covers both. Over the years they have increased private equity and foreign stocks and reduced real estate and domestic stocks.
The Average Hedge Fund No Longer Produces Alpha
I regressed the excess (above risk free rate) monthly returns of the HFRI fund-weighted hedge fund index on the excess returns of the MSCI All Country World Index (gross returns):
Back at the turn of the century, the hedge fund index had alpha between 5 and 10%. But it collapsed going into the financial crisis and in the most recent 5 year period alpha is -0.17% p.a. Beta is 0.34. The r-squared between the MSCI and HFRI excess returns is 0.86, which is high. So, you might as well invest 34% of your money in global stocks and the rest in cash to replicate the index. Interestingly, a linear trend line rather than an exponential trend line fits the index:
So, it doesn't make sense to invest in hedge funds recently unless you can select an above average fund.
Back at the turn of the century, the hedge fund index had alpha between 5 and 10%. But it collapsed going into the financial crisis and in the most recent 5 year period alpha is -0.17% p.a. Beta is 0.34. The r-squared between the MSCI and HFRI excess returns is 0.86, which is high. So, you might as well invest 34% of your money in global stocks and the rest in cash to replicate the index. Interestingly, a linear trend line rather than an exponential trend line fits the index:
So, it doesn't make sense to invest in hedge funds recently unless you can select an above average fund.
Friday, January 18, 2019
All of Labor's Tax Increases
The Labor party is at the moment likely to win the next federal election in Australia in May. Labor has become increasingly left wing in recent years and has a long list of policies to raise taxes. This is, I think, a comprehensive list:
- Abolish Liberal plan to raise the top tax threshold to $200k: This was supposed to happen in 2024. The top tax bracket will still cut in at $180k (about USD130k) where it has been for many years. Bracket creep is pushing more and more taxpayers into the top bracket. This will affect us if I am still working then. If I'm not, probably my taxable income will be lower.
- Raise the top tax rate: Add 2% to the top rate to raise it to 47%. With Medicare that is 49%. This will immediately raise our taxes.
- Abolish plan to eliminate 37% tax bracket: This also was supposed to happen in 2024, so may not affect us except to the extent of how many franking credits will get used up offsetting our taxes, if I retire by then.
- Repeal already-legislated tax cuts for companies with turnovers of between $10 million and $50 million: Small businesses pay 27.5% corporation tax and larger companies 30%. The government wanted to extend the low rate to larger companies. This is unlikely to directly affect us.
- Reduce the long-term capital gains tax discount to 25%: The discount is now 50%. This will have an immediate impact on us as we have run out of accumulated tax losses. OTOH existing investments will be grandfathered. It makes it more attractive to incorporate and pay CGT of 27.5% instead of 37.5%.
- Abolish refundability of franking credits: Since 2000, if you have excess tax credits from Australian companies beyond those that offset the taxes you need to pay you can get a cash refund. I did benefit from this once or twice soon after we moved to Australia and my income was low. This will have a big impact on superannuation funds in pension phase that have zero tax to pay and possibly even in accumulation phase if they have a lot of franked dividends. It will affect lower income self-funded retirees with money outside superannuation too. Some listed investment companies (closed end funds) are already paying out special dividends to get franking credits out of the fund and to investors before the end of the financial year. On the other hand, I don't think these funds will radically restructure due to this proposal. I don't think it will have a big impact on us as I've planned to put the least tax advantaged investments like managed futures into our planned SMSF. And I expect we would be in the 32.5% tax bracket when retired. If I retire at 60 say and start a superannuation pension we could use franking credits inside our SMSF to offset Moominmama's superannuation earnings tax liability as she is 10 years younger. And then maybe we could add Moomin to the superannuation fund :)
- Abolish negative gearing: This is the ability to deduct investment costs beyond the earnings of an investment from other income. This mainly applies to property investors who mostly lose money in Australia in the short run, hoping for a long-run capital gain. We don't negative gear so it shouldn't affect us. Wealthier property investors who also own shares or other investments will be able to offset their losses in property against dividend and other income. So, like many of the Labor measures they mainly hit lower income investors...
- Tax discretionary trusts as companies: These are trusts that have multiple beneficiaries and can alter what earnings they stream to which beneficiary on a year by year basis. Actually, they are proposing to tax trust distributions at a minimum of 30%. So, it's not like a company which pays 27.5% tax in the case of a small business and then distributes franking credits. I don't see any justification for allowing this kind of tax dodging. However, I think they should just require all trusts to be unit trusts with defined shares and everyone sharing in all income. These operate just like unlisted managed funds (mutual funds). I think most discretionary trusts will just do this if it's allowed.
- Reduce annual non-concessional superannuation contributions to $75k: This would mean it would take us more years to make all the non-concessional contributions we want to make and means I probably should already get one in this financial year.
- Reduce the threshold for 30% superannuation contributions tax to $200k: Currently the threshold is $250k. The threshold includes employer superannuation contributions, so this will definitely affect me.
- Remove the right, already legislated by the government, of
superannuants to make catch-up contributions when their super balance is
less than $500,000: I don't think this is probably a big deal. It will mean stretching contributions over more years.
- Reduce ability to take tax deductions for additional concessional superannuation contributions: People will need to have 90% of their income or more from sources other than employment to do this. I don't understand why concessional contributions for employees are limited to salary-sacrificed contributions and you can't make more concessional contributions unless you really aren't an employee. The Liberals tried to fix this anomaly.
- Limit tax free pensions to $75k per year: Currently you can transfer up to $1.6 million into an account to fund a tax free superannuation pension. At a 4% initial withdrawal rate (required rate for under 65s) that is $64k per year. At 5% (65-74 y.o.) it is $80k per year. So, Labor's proposal is not that restrictive. However, if the $1.6 million earns a lot more than that a year, it will be taxed a lot more than at present.
- Limit deductions for tax advice to $3,000 per year: I am assuming that this won't apply to companies or superannuation funds, just to individuals. In which case, it isn't a big deal.
Thursday, January 17, 2019
David Svensen Lecture at Yale
Svensen is the manager of Yale's endowment. He also gives occasional lectures at Yale.
My investment strategy is strongly influenced by endowment investors like Svensen.
My investment strategy is strongly influenced by endowment investors like Svensen.
Wednesday, January 16, 2019
Moomin Needs a Tax File Number
That's what the bank in Falafelland says... So, I will look today at applying for one for him. I think they should just give them out when you apply for a birth certificate. I don't know if the bank wants it because they just want a permanent ID for him or because it will affect the tax he pays as a foreign beneficiary of a local trust account. Up till now we have been using his passport number as an ID number. But passport numbers aren't permanent. You get assigned a new one every time you renew your passport, which is every 5 years for children.
Saturday, January 12, 2019
Portfolio Charts
Portfolio Charts is a really interesting website where you can do simulations of safe and permanent withdrawal rates and many other things for a range of investment portfolios. These include predefined portfolios and you can also build your own portfolio using a range of ETFs. Here for example is Tony Robbins' version of Ray Dalio's All Weather portfolio:
The orange line gives the withdrawal rate which means that you wouldn't have run out of money if you retired in any year since 1970 and retired for the length of time on the x-axis. The green line is the withdrawal rate that means that you will have at least as much money as you started with in real terms. It's interesting how these go in opposite directions as the length of retirement increases. If you retired for 30 years the permanent withdrawal rate is 3.8%. This portfolio had an average real return of 5.5%. The best performing portfolio in terms of withdrawal rates is the site creator's own "Golden Butterfly" which has 40% stocks, 40% bonds, and 20% gold:
This portfolio had a real return of 6.5%.
An interesting point is that safe and permanent withdrawal rates vary a lot by country. The site allows you to choose the US, UK, Canada, and Germany as home countries. The linked article also includes Australia, but unfortunately the site itself doesn't allow you to do analysis for Australia. A big caveat is, of course, that all this depends on historical returns. If bonds, for example, don't do as well going forward as they did from 1980 till recently then, withdrawal rates are going to be lower. Choice of alternative investments is also limited to gold, a commodities ETF, and a REIT ETF.
The orange line gives the withdrawal rate which means that you wouldn't have run out of money if you retired in any year since 1970 and retired for the length of time on the x-axis. The green line is the withdrawal rate that means that you will have at least as much money as you started with in real terms. It's interesting how these go in opposite directions as the length of retirement increases. If you retired for 30 years the permanent withdrawal rate is 3.8%. This portfolio had an average real return of 5.5%. The best performing portfolio in terms of withdrawal rates is the site creator's own "Golden Butterfly" which has 40% stocks, 40% bonds, and 20% gold:
This portfolio had a real return of 6.5%.
An interesting point is that safe and permanent withdrawal rates vary a lot by country. The site allows you to choose the US, UK, Canada, and Germany as home countries. The linked article also includes Australia, but unfortunately the site itself doesn't allow you to do analysis for Australia. A big caveat is, of course, that all this depends on historical returns. If bonds, for example, don't do as well going forward as they did from 1980 till recently then, withdrawal rates are going to be lower. Choice of alternative investments is also limited to gold, a commodities ETF, and a REIT ETF.
Annual Report 2018
Investment Returns
In Australian Dollar terms we gained 2.3% for the year while the MSCI gained 0.9% and the ASX200 lost 1.1% (all pre-tax including dividends). In USD terms we lost 7.7%, while the MSCI lost 8.9% and the S&P500 lost 4.4%. So we beat Australian and international markets but not the US market. In the longer term perspective, our returns and market returns were closely aligned this year:
Here are returns over various standard periods (not annualized):
We have done well compared to the ASX 200 over the last 5 years. Not as great over 10 years. In USD terms we have done well compared to the MSCI over the last three years and underperformed over longer time periods.
Investment Allocation
The main change in allocation over the year is the large increase in cash and real estate when we received the inheritance:
I also reduced my allocation to Australian large cap stocks around the same time, in early October. Earlier in the year, the allocation to cash falls as we increased trading and invested more in the Winton Global Alpha Fund (commodities) and subscribed to some IPOs. Private equity also increased with investment in Aura and IPE and then decreased with the takeover of IPE.
Accounts
I stopped reporting monthly accounts this year, but I've still been computing them. Here are our annual accounts in Australian Dollars without including the inheritance:
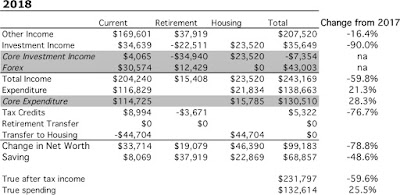
We earned $170k after tax in salary, business related refunds, medical payment refunds, tax refunds etc. We earned (pre-tax including unrealised capital gains) $35k on non-retirement account investments. Both of those numbers were down strongly from last year. I stepped down from an admin role that paid extra salary and earned less in consulting etc. The investment numbers would have been worse without trading and the fall in the Australian Dollar ($31k in "forex" gain). Total current after tax income was $204k. Not including mortgage interest we spent $117k – Total actual spending including mortgage interest was $133k.
$9k of the current pre-tax investment income was tax credits – we don't actually get that money so we need to deduct it. Finally, we transferred $45k in mortgage payments (and virtual saved interest) to the housing account. The change in current net worth, was therefore $34k. Looking at just saving from non-investment income, we saved $8k. Both these numbers are down steeply from last year.
The retirement account is a bit simpler. We made $38k in contributions (after the 15% contribution tax) and the value fell by an estimated $23k in pre tax returns. $4k in "tax credits" is an adjustment needed to get from the number I calculate as a pre-tax return to the after tax number. Taxe on returns are just estimated because all we get to see is the after tax returns. I do this exercise to make retirement and non-retirement returns comparable. Net worth of retirement accounts increased by $19k.
Finally, the housing account. We spent $16k on mortgage interest. We would have paid $24k in mortgage interest if we didn't have an offset account. I estimate our house is worth $24k more than I did last year based on recent sales in our neighbourhood. After counting the transfer of $45k into the housing account housing equity increased $46k of which $23k was due to paying off principal on our mortgage.
Total net worth increased by $99k, $69k of which was saving from non-investment sources. Comparing 2018's accounts with 2017's, we saved 49% less and net worth increased by 79% less. Total after tax income was almost $230k, down 60% on last year. This number feels a lot more "reasonable" than last year.
Though our saving is down sharply on last year, we still saved in total 33% of our after tax non-investment income. Of course, this is less than last year's 50%. Including investment income our savings rate was 43%.
Here are the same accounts expressed in US Dollars:
How Does This Compare to My Projection for This Year?
At the beginning of the year, I projected a gain in net worth of $250k based on an 8% return on investments and a 6% increase in spending. As you can see, spending rose 25% and return on investments was only 2%. As a result net worth increased by only $99k.
Looking to 2019, I think we will be lucky if our investment return is 0%, as I am quite bearish about the world economy and stockmarket. If I pencil in a 6% rise in spending, then we would only increase net worth by $60k.
In Australian Dollar terms we gained 2.3% for the year while the MSCI gained 0.9% and the ASX200 lost 1.1% (all pre-tax including dividends). In USD terms we lost 7.7%, while the MSCI lost 8.9% and the S&P500 lost 4.4%. So we beat Australian and international markets but not the US market. In the longer term perspective, our returns and market returns were closely aligned this year:
Australian Dollar Returns
Here are returns over various standard periods (not annualized):
We have done well compared to the ASX 200 over the last 5 years. Not as great over 10 years. In USD terms we have done well compared to the MSCI over the last three years and underperformed over longer time periods.
Investment Allocation
The main change in allocation over the year is the large increase in cash and real estate when we received the inheritance:
I also reduced my allocation to Australian large cap stocks around the same time, in early October. Earlier in the year, the allocation to cash falls as we increased trading and invested more in the Winton Global Alpha Fund (commodities) and subscribed to some IPOs. Private equity also increased with investment in Aura and IPE and then decreased with the takeover of IPE.
Accounts
I stopped reporting monthly accounts this year, but I've still been computing them. Here are our annual accounts in Australian Dollars without including the inheritance:
Annual Accounts
There are lots of quirks in the way I compute the accounts, which have gradually evolved over time. Here is an explanation:
Current account is all
non-retirement accounts and housing account income and spending. Then
the other two are fairly self-explanatory. But housing spending only
includes mortgage interest. Property taxes etc. are included in the
current account. There is not a lot of logic to this except the
"transfer to housing" is measured using the transfer from our checking
account to our mortgage account. Current other income is reported after
tax, while investment income is reported pre-tax. Net tax on investment
income then gets subtracted from current income as our annual tax refund
or extra payment gets included there. Retirement investment income gets
reported pre-tax too while retirement contributions are after tax. For
retirement accounts, "tax credits" is the imputed tax on investment
earnings which is used to compute pre-tax earnings from the actual
received amounts. For non-retirement accounts, "tax credits" are actual franking credits
received on Australian dividends and the tax withheld on foreign
investment income. Both of these are included in the pre-tax earning but
are not actually received month to month as cash.... Finally, "core
expenditure" for housing is the actual mortgage interest we paid.
"Expenditure" adds back how much interest we saved by keeping money in
our offset account.
We include that saved interest in the current account as the earnings
of that pile of cash. That virtual earning needs to be spent somewhere
to balance the accounts... It is also included in the "transfer to
housing". Our actual mortgage payments were less than the number
reported by the $6k in saved interest. For current accounts "core
expenditure" takes out business expenses that will be refunded by our
employers and some one-off expenditures. This year, I think there are
none of those one-off expenditures. "Saving" is the difference
between "other income" net of transfers to other columns and spending in
that column, while "change in net worth" also includes the investment
income.
We earned $170k after tax in salary, business related refunds, medical payment refunds, tax refunds etc. We earned (pre-tax including unrealised capital gains) $35k on non-retirement account investments. Both of those numbers were down strongly from last year. I stepped down from an admin role that paid extra salary and earned less in consulting etc. The investment numbers would have been worse without trading and the fall in the Australian Dollar ($31k in "forex" gain). Total current after tax income was $204k. Not including mortgage interest we spent $117k – Total actual spending including mortgage interest was $133k.
$9k of the current pre-tax investment income was tax credits – we don't actually get that money so we need to deduct it. Finally, we transferred $45k in mortgage payments (and virtual saved interest) to the housing account. The change in current net worth, was therefore $34k. Looking at just saving from non-investment income, we saved $8k. Both these numbers are down steeply from last year.
The retirement account is a bit simpler. We made $38k in contributions (after the 15% contribution tax) and the value fell by an estimated $23k in pre tax returns. $4k in "tax credits" is an adjustment needed to get from the number I calculate as a pre-tax return to the after tax number. Taxe on returns are just estimated because all we get to see is the after tax returns. I do this exercise to make retirement and non-retirement returns comparable. Net worth of retirement accounts increased by $19k.
Finally, the housing account. We spent $16k on mortgage interest. We would have paid $24k in mortgage interest if we didn't have an offset account. I estimate our house is worth $24k more than I did last year based on recent sales in our neighbourhood. After counting the transfer of $45k into the housing account housing equity increased $46k of which $23k was due to paying off principal on our mortgage.
Total net worth increased by $99k, $69k of which was saving from non-investment sources. Comparing 2018's accounts with 2017's, we saved 49% less and net worth increased by 79% less. Total after tax income was almost $230k, down 60% on last year. This number feels a lot more "reasonable" than last year.
Though our saving is down sharply on last year, we still saved in total 33% of our after tax non-investment income. Of course, this is less than last year's 50%. Including investment income our savings rate was 43%.
Here are the same accounts expressed in US Dollars:
How Does This Compare to My Projection for This Year?
At the beginning of the year, I projected a gain in net worth of $250k based on an 8% return on investments and a 6% increase in spending. As you can see, spending rose 25% and return on investments was only 2%. As a result net worth increased by only $99k.
Looking to 2019, I think we will be lucky if our investment return is 0%, as I am quite bearish about the world economy and stockmarket. If I pencil in a 6% rise in spending, then we would only increase net worth by $60k.
New Investment: U.S. Treasury Bills
Interactive Brokers currently pays 1.7% interest on U.S. Dollars. But U.S. government bonds pay more than that and are supposedly risk free, so I thought I would give it a try. I am concerned that U.S. interest rates could still rise and so I don't want longer term bonds. So, I just bought a U.S. Treasury Bill expiring on 12 February. My idea is when that matures, I'll put part of the proceeds towards buying Australian Dollars. I plan to build a ladder of these and so force myself to buy Australian Dollars slowly.
At IB the commission for buying bonds is $5 and it turns out that the minimum trade size for treasuries is $100k. This isn't stated anywhere, but when I tried buying $50k last week, I got a message that my trade size was too small, whereas this trade went through. I'm gradually moving U.S. Dollars to my IB account - I can move up to $100k every 7 business days using the ACH method.
I've thought about municipal and corporate bonds too, but these can be illiquid. For example, for the nearest term Berkshire Hathaway bond, only $1000 is currently being offered.
At IB the commission for buying bonds is $5 and it turns out that the minimum trade size for treasuries is $100k. This isn't stated anywhere, but when I tried buying $50k last week, I got a message that my trade size was too small, whereas this trade went through. I'm gradually moving U.S. Dollars to my IB account - I can move up to $100k every 7 business days using the ACH method.
I've thought about municipal and corporate bonds too, but these can be illiquid. For example, for the nearest term Berkshire Hathaway bond, only $1000 is currently being offered.
Wednesday, January 09, 2019
Investment Policy for Trust Accounts
My brother is opening the trust accounts. They will be invested in local mutual funds. Unlike Australian or US managed or mutual funds these do not make distributions but like an Australian listed investment company (closed end fund) they pay tax on their earnings. The tax though is the relevant investment rate not the corporation tax. This is 25% of the inflation adjusted gain. Also, if you sell a mutual fund in Falafelland 25% capital gains tax is withheld. Looks like we can't really avoid this tax. Foreign tax paid is not refundable as cash in Australia – it can only be deducted against Australian tax liable.* Because my son's earnings would be way below the tax free threshold (initially each of these accounts will have about AUD 44k in them) he wouldn't need to pay tax if the investment funds were based in Australia.
My brother suggested investing 70% in bonds and 30% in stocks. As a long-term investment policy – we will be investing for the next 20 years for my son – I think this is too conservative.
This is both because in the long run stocks have performed better than bonds in most countries but also because interest rates are now low. This chart shows the real returns on US investments over the last century:
Since 1980, bonds did well as interest rates fell from historic highs. But in the 40 years up to 1980 bonds lost money in real terms as interest rates rose. So, I told him if we are adopting a "set and forget" investment policy then we should go for 60% stocks and 40% bonds. The mix between local and international investments should be 50/50. The local market is one of the cheaper ones globally.
OTOH the local currency is quite strong currently. If we can revisit investment policy periodically then 70% bonds is OK for now. If there is a future larger decline in stock markets we would then switch to a more aggressive stance.
My brother's children are much older and so their trust accounts will exist for less time. If they intend to spend the money when they get it then I guess a more conservative stance might make sense. The youngest though will still need to wait 9 years to get her money so I think she can be more aggressive.
* Labor wants to make franking credits from Australian companies non-refundable as well. This would bring back symmetry in the way these credits are treated. Of course, I think we should go in the other direction and make foreign tax refundable :)
My brother suggested investing 70% in bonds and 30% in stocks. As a long-term investment policy – we will be investing for the next 20 years for my son – I think this is too conservative.
This is both because in the long run stocks have performed better than bonds in most countries but also because interest rates are now low. This chart shows the real returns on US investments over the last century:
Since 1980, bonds did well as interest rates fell from historic highs. But in the 40 years up to 1980 bonds lost money in real terms as interest rates rose. So, I told him if we are adopting a "set and forget" investment policy then we should go for 60% stocks and 40% bonds. The mix between local and international investments should be 50/50. The local market is one of the cheaper ones globally.
OTOH the local currency is quite strong currently. If we can revisit investment policy periodically then 70% bonds is OK for now. If there is a future larger decline in stock markets we would then switch to a more aggressive stance.
My brother's children are much older and so their trust accounts will exist for less time. If they intend to spend the money when they get it then I guess a more conservative stance might make sense. The youngest though will still need to wait 9 years to get her money so I think she can be more aggressive.
* Labor wants to make franking credits from Australian companies non-refundable as well. This would bring back symmetry in the way these credits are treated. Of course, I think we should go in the other direction and make foreign tax refundable :)
Target Portfoilo Performance December 2018
In AUD terms the target portfolio lost 1.85% in December, gaining 0.3% for 2018 as a whole. The MSCI gained 0.9% for the year and I gained 2.3%. The graph shows the returns for the each month in 2018 for the target portfolio, the MSCI World Index in AUD terms, and the target portfolio:
The target has lower volatility but is more correlated to the MSCI than I was. So the target portfolio wouldn't have provided very useful diversification in 2018.
The target has lower volatility but is more correlated to the MSCI than I was. So the target portfolio wouldn't have provided very useful diversification in 2018.
Friday, January 04, 2019
Crowdfunded Real Estate
A relatively new investment concept is crowdfunding real estate investments. The idea is that an individual could directly invest small amounts in a range of properties or development opportunities thus reducing their risk. Rather than a fund manager picking the properties, investors could evaluate deals themselves.
I read about Fundrise on Financial Samurai. It seems to actually be closer to a traditional unlisted real estate managed fund, except there is more of a property development angle. They allow investments in both real estate debt and equity. They claim very high historical rates of return. I find it hard to understand how they could be so high. Equity investments could have leverage but debt investments must return the interest rate on the mortgage minus costs? I didn't feel that there was enough transparency around how returns are generated. In any case, unfortunately, it is not open to non-US investors.
So, I looked for crowdfunded real estate opportunities in Australia. This is what I found:
Crowdfundup – I only found one active project on the site.
Estatebaron – This website has more active deals. It focuses exclusively on property development. There seems to be very little information about each project and the site is much less polished.
Brickraise – The link seems to be dead.
Domacom – This is an ASX listed company. The company looked like they were heading to bankruptcy before a recent fundraising. The new money will only last just over half a year as their burn rate is AUD 5 million a year. They will need more than AUD 0.5 billion assets under management to break even given a 0.8% of NAV management fee. However, they have the largest number of deals on their site and have high quality information. Deals include a wide range of projects including solar farms and bioenergy as well as more conventional real estate. This is something I might consider when we have an SMSF up and running if it looks like the company will survive.
Based on this, real estate crowdfunding is not well developed in Australia. Do you know of other better websites?
Thursday, January 03, 2019
New Investment: PERLS XI
As a place to park Australian Dollars cash until I can move it out of Interactive Brokers, I bought some PERLS XI hybrid bank securities. These are Commonwealth Bank bonds that instead of paying interest pay franked dividends. The "grossed up" rate is 5.7% p.a. roughly. At some point the bonds should convert into Commonwealth Bank shares. However, the conversion rate isn't pre-determined. Instead, $100 of bonds will convert to $100 of shares at whatever the share price is at that time. I thought this was better than earning only 1.4% interest on my money, though there is a risk that the capital value will fall if interest rates rise in Australia. That doesn't look very likely at the moment to me. They are in theory less safe than bank deposits, but the risk of Commonwealth Bank getting into bad enough financial trouble in the next few months to reduce the value seems extremely low to me.
I think this is the first time I have ever bought bonds directly for my own account.
Insane Moves in Australian Dollar and Yen This Morning
Moves this big never happen in currencies. It's like one month's worth of moves in 5 minutes. Yen did the same thing in the other direction, other currencies not so much. No idea what sparked this. I managed to buy AUD24k...
This is being called a "flash crash".
Wednesday, January 02, 2019
December 2018 Report
You'll probably have heard that this was the worst December for US stocks since 1931. December is seasonally a positive month for stocks. Things weren't quite that bad in Australia and because the Australian Dollar fell, our returns for the month in AUD terms ended up being positive.
The Australian Dollar fell from USD 0.7302 to AUD 0.7049 The MSCI World Index fell 7.00% and the S&P 500 9.03%. The ASX 200 fell only 0.01%. All these are total returns including dividends. We gained 0.24% in Australian Dollar terms and lost 3.24% in US Dollar terms. So, we outperformed the Australian and international markets. This is not surprising given the weight of US Dollar cash in our portfolio. Our currency neutral rate of return was -1.74%.
Here again is a detailed report on the performance of all investments:
Things that worked quite well this month:
- US Dollars cash
- Gold
- Property, including:
- My jointly owned apartment with my brother. We got an offer for the apartment near the end of the month and I raised the carrying value in line with that.
- TIAA (direct US investments) and Pendal (REITS) real estate funds.
- On the other hand BlueSky lost a lot...
- Our direct share holdings in Medibank and Yellowbrickroad.
- Again, the PSS(AP) superannuation fund did relatively well (though losing) compared to Unisuper. But on the way up it gained just as much as Unisuper. It has both lower beta and higher alpha... At least based on the investment choices I have made within the fund.
What really didn't work:
- Cadence Capital, again fell sharply. It's performance in the last three months has been very bad. It's not surprising that they have cancelled their IPO of the Cadence Opportunities Fund. They received only AUD 8 million of subscriptions. It will still go ahead as an unlisted public company, whatever that is. Overall, we have lost money investing in Cadence.
- BlueSky fell back too. We still have made some money on this investment.
- 3i, China Fund, Pershing Square, and CFS Geared Global Shares all fell in line with global stock markets. The latter would have benefited from the fall in the Australian Dollar, which for an investment denominated in Australian Dollars is included in the return on that investment, but is separated out for the investments denominated in foreign currency...
We also invest AUD 2k monthly in a set of managed funds, and there are also retirement contributions. Then there are distributions from funds and dividends. Other moves this month:
- I bought 400 shares of the China Fund (CHN) early in the month. Not a good idea.
- I bought 25,000 shares of Bluesky Alternatives in the middle of the month (BAF.AX). Another bad idea.
- I bought 500 shares of Pershing Square Holdings (PSH.L) at the end of the month. So far, not a bad idea.
- I received cash from UBS in my US bank account and started moving it to Interactive Brokers and from there to our Australian bank account. After this first transfer, most of this money will go into buying a US Treasury Bills ladder in the short run. Today, I discovered that I have to keep the cash at IB for 2 months before I can move it to another bank account. So I am looking to buy some Australian bonds (probably bank hybrid securities) in the interim.
Tuesday, December 25, 2018
What's Your Forecast for the Stock Market?
My brother asked me what my forecast for the stock market was. Here is what I wrote to him:
"Well, I’ve been surprised how weak it has been recently, particularly in December, which you may have heard is so far the worst December in US stock markets since 1931. December is a seasonally strong month as is January. The US economy has been strong though house prices have been falling in many places, presumably due to the Fed raising interest rates and this seems to have been the main reason why the market is down. House prices have been falling in Sydney and Melbourne without any increase in interest rates here. Some indicators though show that the global economy could already be in recession, but I don’t know how reliable that is. The reason I was a bit surprised was it has been very predictable that before recessions the yield curve would invert (short term interest rates higher than long term). This hasn’t happened yet in the US. However, the Fed is signalling that they are going to raise interest rates by another 0.5% in 2019 which would reach an inversion probably. Stock markets tend to be leading indicators and so looks like this time it is more leading than usual. The US economic expansion is the 2nd longest in history and so presumably would come to an end some time soon (Australia hasn’t had a recession since the early 90s though…). Now we can say that the bull market ended as stocks have fallen 20%. If we look at the last two recessions and stock market crashes in the US, the stock market bottomed near the end or after the actual recession – in March 2003 and 2009. At that point the Fed will have slashed interest rates dramatically and unemployment will be high. OTOH in the 1990s the US market bottomed in October 1990, which was when the recession was only just getting underway. The Gulf War turned that around.
I did reduce my exposure to the stock market in early October, but not by enough. So, I’d probably use rallies in the market to reduce exposure more at this point. I was planning to use trading as a hedge, but I stopped trading soon after that as backtests weren’t good and I got ill and didn’t have time to work on it.
Of course, I could be completely wrong about all of this. In the last cycle I got out too early and got back in too early. Probably this time I’ll be late :)
I’m not planning on buying Australian Dollars in a hurry either, even though the current price is quite good. I’ll buy them gradually."
"Well, I’ve been surprised how weak it has been recently, particularly in December, which you may have heard is so far the worst December in US stock markets since 1931. December is a seasonally strong month as is January. The US economy has been strong though house prices have been falling in many places, presumably due to the Fed raising interest rates and this seems to have been the main reason why the market is down. House prices have been falling in Sydney and Melbourne without any increase in interest rates here. Some indicators though show that the global economy could already be in recession, but I don’t know how reliable that is. The reason I was a bit surprised was it has been very predictable that before recessions the yield curve would invert (short term interest rates higher than long term). This hasn’t happened yet in the US. However, the Fed is signalling that they are going to raise interest rates by another 0.5% in 2019 which would reach an inversion probably. Stock markets tend to be leading indicators and so looks like this time it is more leading than usual. The US economic expansion is the 2nd longest in history and so presumably would come to an end some time soon (Australia hasn’t had a recession since the early 90s though…). Now we can say that the bull market ended as stocks have fallen 20%. If we look at the last two recessions and stock market crashes in the US, the stock market bottomed near the end or after the actual recession – in March 2003 and 2009. At that point the Fed will have slashed interest rates dramatically and unemployment will be high. OTOH in the 1990s the US market bottomed in October 1990, which was when the recession was only just getting underway. The Gulf War turned that around.
I did reduce my exposure to the stock market in early October, but not by enough. So, I’d probably use rallies in the market to reduce exposure more at this point. I was planning to use trading as a hedge, but I stopped trading soon after that as backtests weren’t good and I got ill and didn’t have time to work on it.
Of course, I could be completely wrong about all of this. In the last cycle I got out too early and got back in too early. Probably this time I’ll be late :)
I’m not planning on buying Australian Dollars in a hurry either, even though the current price is quite good. I’ll buy them gradually."
Friday, December 21, 2018
No Interest on More Than $2 Million Deposit?
My brother and I have between us more than USD 2 million in cash in an account at UBS – most of the money we inherited – that we have been jumping through hoops to get out of there. In the meantime the bank seems to be paying no interest on the money and in the last two weeks it actually the account went down by USD 800 for no clear reason – online I can't find any info on fees the bank has charged. How is that possible?
Looks like we have everything in place now to close the account but have been told it'll take about 2 weeks still given the coming holidays etc. However, the client manager told my brother that she could transfer the majority of the money to us right away, while keeping some for unspecified fees and sending us the remainder not spent on fees later. My brother told her that he was happy to wait to get the money in one lump when they close the account. I was shocked and told him to accept her offer. It's hard for me to imagine that the extra fees for a second transfer could be more than the interest we could potentially earn on the money in two weeks (c. USD 2,000 if investing in US Treasury bills).
Update: We missed the client manager leaving for the Christmas break, so likely won't be till mid-January that we'll get the money out...
Another update: Actually, we now got about 90% of the money transferred to us. Why they need to hang on to a 1/4 million dollars, I don't know...
Looks like we have everything in place now to close the account but have been told it'll take about 2 weeks still given the coming holidays etc. However, the client manager told my brother that she could transfer the majority of the money to us right away, while keeping some for unspecified fees and sending us the remainder not spent on fees later. My brother told her that he was happy to wait to get the money in one lump when they close the account. I was shocked and told him to accept her offer. It's hard for me to imagine that the extra fees for a second transfer could be more than the interest we could potentially earn on the money in two weeks (c. USD 2,000 if investing in US Treasury bills).
Update: We missed the client manager leaving for the Christmas break, so likely won't be till mid-January that we'll get the money out...
Another update: Actually, we now got about 90% of the money transferred to us. Why they need to hang on to a 1/4 million dollars, I don't know...
Monday, December 17, 2018
Will Listed Investment Companies Restructure if Labor Eliminates Refundability of Franking Credits?
As you probably know if you live in Australia, Labor plans to abolish the refundability of franking credits - the tax credits attached to dividends for company tax already paid. This will affect taxpayers with low marginal tax rates including self managed superfunds that are paying out a pension, which is tax free if they have less than AUD 1.6 million in assets for that member. This could significantly cut the retirement income of self-funded retirees who have a lot of Australian shares. OTOH, this was the policy prior to 2000 and most other offsets, like foreign tax credits, aren't refundable either.
I already plan to have relatively small amounts of Australian shares when I start an SMSF - this makes sense as I have lots of investments outside super and so it makes sense to put the least tax efficient investments like managed futures into super.
Listed investment companies (LICs) are closed-end funds that pay tax on their earnings and then distribute franked dividends to shareholders. I own shares in several of these like Platinum Capital, Cadence Capital, Hearts and Minds, and Tribeca Global Resources. Both Geoff Wilson and Cadence Capital's Karl Siegling have suggested that they will reorganize their funds if this happens. There are a couple of ways this could happen. One I had thought about, is to delist and turn the fund into a unlisted managed fund (mutual fund). For funds that trade at a premium to NAV, like several of Wilson's funds, this would cause investors to lose a lot of money as now their holdings would only be worth the NAV. For funds trading at a discount to NAV it could be attractive, as shareholders would gain wealth (but see below). To the extent that the funds receive franked dividends from companies, they would still have to distribute franking credits, but capital gains would no longer create franking credits.
Another option I didn't know about, is that they could instead convert to a listed investment trust like an ETF that doesn't pay taxes. This solves the problem of wealth destruction for funds trading at a premium to NAV.
But the article I linked says that this would result in realization of the portfolio for tax purposes. This could be a huge tax bill for companies like Argo that do little trading. The funds will need to pay out a massive special dividend to distribute the associated franking credit. According to Argo's website they will need to pay 72 cents in tax for liquidating the portfolio. That means they would have to pay a $1.68 cash dividend and so actually sell 23% of the portfolio to pay the dividend out. Some other funds have undistributed franking credits and so would also need to sell shares to generate the cash for such a dividend. They will need to do this soon, as there will probably be an election next May. So, I am a bit skeptical that many will.
I already plan to have relatively small amounts of Australian shares when I start an SMSF - this makes sense as I have lots of investments outside super and so it makes sense to put the least tax efficient investments like managed futures into super.
Listed investment companies (LICs) are closed-end funds that pay tax on their earnings and then distribute franked dividends to shareholders. I own shares in several of these like Platinum Capital, Cadence Capital, Hearts and Minds, and Tribeca Global Resources. Both Geoff Wilson and Cadence Capital's Karl Siegling have suggested that they will reorganize their funds if this happens. There are a couple of ways this could happen. One I had thought about, is to delist and turn the fund into a unlisted managed fund (mutual fund). For funds that trade at a premium to NAV, like several of Wilson's funds, this would cause investors to lose a lot of money as now their holdings would only be worth the NAV. For funds trading at a discount to NAV it could be attractive, as shareholders would gain wealth (but see below). To the extent that the funds receive franked dividends from companies, they would still have to distribute franking credits, but capital gains would no longer create franking credits.
Another option I didn't know about, is that they could instead convert to a listed investment trust like an ETF that doesn't pay taxes. This solves the problem of wealth destruction for funds trading at a premium to NAV.
But the article I linked says that this would result in realization of the portfolio for tax purposes. This could be a huge tax bill for companies like Argo that do little trading. The funds will need to pay out a massive special dividend to distribute the associated franking credit. According to Argo's website they will need to pay 72 cents in tax for liquidating the portfolio. That means they would have to pay a $1.68 cash dividend and so actually sell 23% of the portfolio to pay the dividend out. Some other funds have undistributed franking credits and so would also need to sell shares to generate the cash for such a dividend. They will need to do this soon, as there will probably be an election next May. So, I am a bit skeptical that many will.
Labels:
australia,
Investment Theory,
Investments,
Planning,
SMSF,
Tax
Sunday, December 09, 2018
Was It a Good Decision to Switch to Defined Contribution Superannuation?
Back in 2009 when I started with my current employer, I carried out a cost-benefit analysis to see whether it made sense to stay in the default defined benefit scheme or to switch to the defined contribution scheme. As a result of the analysis I switched to defined contribution.
Was that a good decision. Using the info in the Unisuper PDS and my data I compute that if I retired at the end of this month I would get a lump sum of AUD 213k. My actual Unisuper account is at AUD 284k. So, so far it's been a good decision.
For context, in Britain, there have been strikes and demonstrations against the plan to switch academics from defined benefit to defined contribution. But I see defined benefit as a regressive form of socialism where people who are promoted near the end of their career suck the benefits from the system. This is because the lump sum benefit is proportional to the members salary in the last 5 years. I've seem quite a few people promoted to professor in their last few years and of course, deans and other senior administrators benefit heavily from the scheme. This is at the expense of successful researchers who are promoted early and stay in research at a more or less constant salary.
Saturday, December 08, 2018
Target Portfoilo Performance November 2018
The target portfolio gained 0.22% in AUD terms. Offsetting losses in Ausrtalian shares, gold, and unhedged foreign shares there were gains in particular in managed futures and buyout PE.
Tuesday, December 04, 2018
FIRE?
I just read what was a controversial blogpost at Financial Samurai:"Why $5 Million Is Barely Enough To Retire Early With A Family". The post analyses the income and expenditure of a family living in west Los Angeles. A lot of commenters are critical of the assumptions and spending behavior of this family and some people provide some alternative numbers. That got me thinking about the numbers for our family in a bit more detail than I had thought about previously. In the following, I assume we retire where we currently live in Canberra, Australia.
Our net worth is only a bit over half that in Ken's blogpost: AUD 4 million (USD 3 million). We spend about AUD 10k (USD 7k per month) including mortgage interest (but not taxes) compared to their USD 14k per month. If we retired, most of our spending would be unchanged. We don't wear fancy clothes to work and we don't commute long distances. Assuming we continue daycare for 3 days a week (a very good idea in my opinion) we would lose the government subsidy, increasing our spending by AUD8k per year. Anyway, we would progress to private pre-school and likely private school after that going forward so we will have schooling expenses of a similar level. Unlike the American case studies, our health insurance would be unchanged at AUD 6k per year. In fact, it would make sense in my opinion to drop the private health cover and rely on the government system as we will no longer need to pay the Medicare Levy Surcharge if we don't have private insurance. Moominmama will probably want to keep the coverage, though, because she thinks private everything is better (see schools above). Also, unlike the US, we don't need to worry about saving for college tuition because almost all Australian universities are public and students borrow the tuition costs from the government and pay it back as their post-graduation income allows.
Another thing that would be more expensive for us is international travel. This year we traveled as a family for a month to three Northern European countries and Japan. As I went to three international conferences, my fare was paid my employer. I also deducted two weeks accommodation for two conferences which were in the same city and half my wife's airfare from our taxes. She also attended one of the conferences. If we had to pay for everything ourselves, it would have cost us about AUD 5k more.
On the income side, if we stop working, our tax will fall to effectively zero. We will put as much as possible into superannuation and two tax-free thresholds and franking credits should mean no tax on the earnings of the "taxable" part of the portfolio. If I get back into trading successfully, we probably will have to pay tax again, but then our income will be higher too.
So AUD 130k or so per year is about 3.25% of the net worth, which is close to ERN's recommended withdrawal rate. So, in theory we could retire now. As, I'm in my mid-50s, this would still qualify as early retirement. However, I am a bit worried about rising expenditure and a looming economic downturn. Also, at the moment I am happy with my job and so it doesn't make sense to sacrifice the salary. So, at least for the next year we won't implement the RE part of FIRE.
Monday, December 03, 2018
November 2018 Report
Volatility in financial markets continued this month but I hardly traded at all and for us it was a fairly quiet month financially with mostly background prep work. The Australian Dollar rose from USD
0.7083 to USD 0.7302 The MSCI World Index rose 1.51% and the S&P 500 2.04%. The ASX 200 fell 1.96%. All these are total returns including dividends. We lost 1.88% in Australian Dollar terms and gained 1.15% in US Dollar terms. So, we outperformed the Australian market and underperformed international markets. Our Australian Dollar returns are now strongly driven by changes in the exchange rate as cash in US Dollars and other currencies are a large part of our portfolio. Our currency neutral rate of return was -0.14%.Here again is a detailed report on the performance of all investments:
- Bluesky Alternatives rose sharply after Geoff Wilson engineered the firing of most of the board and Pinnacle Investment withdrew their proposal to manage the fund. It now looks like Wilson Asset Management will end up managing the fund. Most Wilson LICs (closed end funds) trade above net asset value.
- The Hearts and Minds IPO started trading and performed well.
- International hedge funds: Tribeca and Pershing each did well in relative terms as did Winton.
- The China Fund had a decent bounce and Boulder Income Fund bounced back very nicely to almost return to it's September value.
- Cadence Capital, again fell sharply. It's performance in the last three months has been very disappointing.
- Perhaps relatedly, small cap Australian funds also performed badly.
- Medibank Private fell sharply after the Australian Defence Department didn't renew its contract with them.
- UK private equity firm, 3i, fell further, though it bounced from its lows.
We also invest AUD 2k monthly in a set of managed funds, and there are also retirement contributions. Then there are distributions from funds and dividends. Other moves this month:
- As mentioned above, Hearts and Minds began to trade and I increased my holding up to the amount I originally requested in the IPO.
- I sold some Platinum Capital (PMC.AX) and bought the equivalent actively managed ETF PIXX.AX instead. The idea was that PMC was overvalued. So far this trade hasn't worked out.
- I bought more Pershing Holdings (PSH.L) and 3i (III.L). Though I increased each position by 50%, each is still only around 0.8% of net worth.
- I did a couple of trades in futures options and futures.
Thursday, November 29, 2018
Put Writing Strategy
ERN recently posted again about his put writing strategy. Despite the market falls in October he ended up for the month. This seems to be down to luck that after his contracts went into the money (which means a loss if you write options) around 12th October, they then recovered substantially before the expiry date.
I was curious about the performance of such a strategy in the long term. You can now buy an ETF that implements a similar strategy. It differs a little from ERN's strategy. In particular, the ETF sells options each month, rather than 3 times a week. It tries to match the performance of the CBOE S&P 500 put writing index. The index goes back to 1986! In the following I analyze the performance of the strategy since January 2007.
Looking at the chart of the index, it seems to track the fluctuations in the stock market quite closely over the last 10 years:
Most of the time there is lower volatility and then there are occasional spikes. When I regress monthly returns on the monthly returns of the S&P 500 total return index (i.e. including dividends) I get a beta of 0.64 and annualized alpha of 0.9%.* The R-squared is 0.74. After transaction costs that alpha will likely disappear. This is looking a lot like investing 64% of your money in an S&P 500 ETF and the rest in cash with occasional volatility spikes added in.
Of course, this might not be much like the return profile that ERN is getting as his performance in October shows.
* This isn't the classic CAPM regression where you deduct the risk free rate first, but that won't make much difference here.
Most of the time there is lower volatility and then there are occasional spikes. When I regress monthly returns on the monthly returns of the S&P 500 total return index (i.e. including dividends) I get a beta of 0.64 and annualized alpha of 0.9%.* The R-squared is 0.74. After transaction costs that alpha will likely disappear. This is looking a lot like investing 64% of your money in an S&P 500 ETF and the rest in cash with occasional volatility spikes added in.
Of course, this might not be much like the return profile that ERN is getting as his performance in October shows.
* This isn't the classic CAPM regression where you deduct the risk free rate first, but that won't make much difference here.
Saturday, November 24, 2018
Trust Accounts
As I mentioned before, my mother's will leaves money for each of her grandchildren – currently six of them including Moomin. They can't get this money until they are 23. The two eldest grandchildren are already 23 or over and so will get their money right away. We now have a clearer picture of what will happen with the other's money. My brother will set up trust accounts with his bank for each of them in his (and my mother's country). These accounts can then invest in any investments they like though probably only through managed funds/shares available in that country. The income will be taxed at source at 25%. I did some research and if we get Moomin a tax file number here in Australia and open a bank account for him, we can submit a tax return each year and get the foreign tax refunded as cash. I used the ATO's tax calculator to check that. As he is inheriting GBP 25k (no, the account isn't in Britain but somewhere to the southeast, let's call it Falafeland :)), the refund might be a few hundred dollars a year. Once he is old enough to understand money a bit he'll be able to decide whether to spend or save that money...
In the meantime, I'm going through the hassle of getting a copy of my passport notarized. This isn't the normal method of proving identity in Australia, which is to go the post office or a police station to get the postal clerk or police officer to stamp and sign the copy as true (actually there is a broad range of people who can do this, including tertiary teachers like me). But this standard certification in Australia isn't valid outside the country, but a "notary public" is needed to certify the document. It seems these people have to be lawyers. Anyway, the bank in Chocolateland (yet another country) wants to get this notarized copy before they will release the main chunk of inherited money to me. Actually, there seem to be four levels of certification available in Australia: regular certification, "justice of the peace" (including police officers), notarization, and an "apostille". Initially, my brother said the Chocolateland bank wanted an apostille...
In the meantime, I'm going through the hassle of getting a copy of my passport notarized. This isn't the normal method of proving identity in Australia, which is to go the post office or a police station to get the postal clerk or police officer to stamp and sign the copy as true (actually there is a broad range of people who can do this, including tertiary teachers like me). But this standard certification in Australia isn't valid outside the country, but a "notary public" is needed to certify the document. It seems these people have to be lawyers. Anyway, the bank in Chocolateland (yet another country) wants to get this notarized copy before they will release the main chunk of inherited money to me. Actually, there seem to be four levels of certification available in Australia: regular certification, "justice of the peace" (including police officers), notarization, and an "apostille". Initially, my brother said the Chocolateland bank wanted an apostille...
Self Managed Superannuation
I am exploring setting up a self managed superannuation fund (SMSF). I want to do this so that I can implement our target portfolio investment strategy and so I can put higher tax investments into the lower tax superannuation environment. Managed futures are a tax ineffective investment outside super when your marginal tax rate is 47%. Inside superannuation they will be taxed at 15%.
Setting up an SMSF is very complicated in Australia compared to the US where you can just open an IRA account with a broker like any other brokerage account and the only issue is limits on contributions and later on minimum withdrawals. For standard IRAs you pay tax on withdrawals only, on your regular tax return. The main reason Australian SMSFs are complex is taxation but some of the bureaucracy just seems to be for the sake of it... In Australia, pretax or concessional contributions are taxed at 15% (or 30% for high income levels) going in, and you can also make after tax contributions. Its necessary to keep track of which were taxed how. Then earnings are taxed at 15% (10% for capital gains) and can be offset by franking credits and foreign tax paid. When you finally withdraw your money, no tax is due and earnings of the account are untaxed if you set up a pension, though now there is a cap of $1.6 million on the amount of assets whose earnings are untaxed. So funds need to submit tax returns separate from their members. And they need to be audited annually and there are lots of ways they could become non-compliant with the rules. And an SMSF is a trust which is set up as a separate legal entity. You might also want to set up a company to act as trustee!
You could go to a lawyer to set up the trust and to a local accountant to help audit the fund and do everything else yourself. But there are many providers who streamline the set up and administration of SMSFs. You can get "year-end" administration which just helps get everything in order for the tax return and audit, or you can get a full daily service. Though I do our own tax returns, I have decided to go for the full daily service as I want to outsource this as much as possible (looks like I am going to have to do tax returns for my son too and am also looking at setting up a company...) and want to be confident that I am compliant with the rules, because the penalties for non-compliance are very severe.
This is a great site with information about different providers of services for self-managed superannuation funds. I visited the websites of all the providers that offer a daily service. Some sites have a lot information and some have next to none. The latter want you to phone them to give you the details. I have a strong preference for financial services that are as transparent as possible. I also investigated Commonwealth Securities and Dixon Advisory, which are not on this list.
Dixon are based in Canberra and I often go past their offices on Northbourne Avenue. Years ago, I used to read Daryl Dixon's column in the Canberra Times. Their service combines admin and investment advice and costs from $3,000 for a $333k account to a maximum of $6,000 for accounts above $666k. To make investments, you have to call their broker and the commissions for shares are 1.1%, which is capped at $400 for Australian shares and uncapped for foreign shares. I don't need investment advice and trading is way too expensive.
Commonwealth Securities is a more realistic option. Including audit fees, they charge a flat $3,000 a year. On a $900k account that is 1/3%, which is reasonable. Trading fees are 0.12% for Australian stocks, which is good though not the lowest, and 0.31% for US stocks and 0.41% for shares in the UK and many other countries, which is expensive but not as outrageous as Dixon. You can't trade CfDs (which are offered by CommSec for other accounts) or futures (which aren't offered by CommSec).
You can set up a trading account for an SMSF with Interactive Brokers, which can trade anything you like for low fees, and then find an administration provider who is prepared to work with them. Determining who can work with IB is what I need to do next. You can trade futures in an SMSF as long as it fits within the written investment strategy (yes, you are required to write one) and other risk related rules.
Two providers on my list, who have won awards and who I am going to investigate next, are Heffron and Super Guardian. I am impressed with the transparent information on Super Guardian's site. They also have an endorsement from Chris Cuffe. Super Guardian charge more the more investments you have. If we have up to 20 investments then they are a similar price to CommSec. Heffron charge a flat fee of $3,300 for their top level service.
Setting up an SMSF is very complicated in Australia compared to the US where you can just open an IRA account with a broker like any other brokerage account and the only issue is limits on contributions and later on minimum withdrawals. For standard IRAs you pay tax on withdrawals only, on your regular tax return. The main reason Australian SMSFs are complex is taxation but some of the bureaucracy just seems to be for the sake of it... In Australia, pretax or concessional contributions are taxed at 15% (or 30% for high income levels) going in, and you can also make after tax contributions. Its necessary to keep track of which were taxed how. Then earnings are taxed at 15% (10% for capital gains) and can be offset by franking credits and foreign tax paid. When you finally withdraw your money, no tax is due and earnings of the account are untaxed if you set up a pension, though now there is a cap of $1.6 million on the amount of assets whose earnings are untaxed. So funds need to submit tax returns separate from their members. And they need to be audited annually and there are lots of ways they could become non-compliant with the rules. And an SMSF is a trust which is set up as a separate legal entity. You might also want to set up a company to act as trustee!
You could go to a lawyer to set up the trust and to a local accountant to help audit the fund and do everything else yourself. But there are many providers who streamline the set up and administration of SMSFs. You can get "year-end" administration which just helps get everything in order for the tax return and audit, or you can get a full daily service. Though I do our own tax returns, I have decided to go for the full daily service as I want to outsource this as much as possible (looks like I am going to have to do tax returns for my son too and am also looking at setting up a company...) and want to be confident that I am compliant with the rules, because the penalties for non-compliance are very severe.
This is a great site with information about different providers of services for self-managed superannuation funds. I visited the websites of all the providers that offer a daily service. Some sites have a lot information and some have next to none. The latter want you to phone them to give you the details. I have a strong preference for financial services that are as transparent as possible. I also investigated Commonwealth Securities and Dixon Advisory, which are not on this list.
Dixon are based in Canberra and I often go past their offices on Northbourne Avenue. Years ago, I used to read Daryl Dixon's column in the Canberra Times. Their service combines admin and investment advice and costs from $3,000 for a $333k account to a maximum of $6,000 for accounts above $666k. To make investments, you have to call their broker and the commissions for shares are 1.1%, which is capped at $400 for Australian shares and uncapped for foreign shares. I don't need investment advice and trading is way too expensive.
Commonwealth Securities is a more realistic option. Including audit fees, they charge a flat $3,000 a year. On a $900k account that is 1/3%, which is reasonable. Trading fees are 0.12% for Australian stocks, which is good though not the lowest, and 0.31% for US stocks and 0.41% for shares in the UK and many other countries, which is expensive but not as outrageous as Dixon. You can't trade CfDs (which are offered by CommSec for other accounts) or futures (which aren't offered by CommSec).
You can set up a trading account for an SMSF with Interactive Brokers, which can trade anything you like for low fees, and then find an administration provider who is prepared to work with them. Determining who can work with IB is what I need to do next. You can trade futures in an SMSF as long as it fits within the written investment strategy (yes, you are required to write one) and other risk related rules.
Two providers on my list, who have won awards and who I am going to investigate next, are Heffron and Super Guardian. I am impressed with the transparent information on Super Guardian's site. They also have an endorsement from Chris Cuffe. Super Guardian charge more the more investments you have. If we have up to 20 investments then they are a similar price to CommSec. Heffron charge a flat fee of $3,300 for their top level service.
Wednesday, November 14, 2018
Regal to Float Hedge Fund LIC on ASX
Regal Funds Management plans to float a hedge fund LIC (closed end fund) on the ASX in March or April next year. Regal was on my future potential investments list but you need to be a certified wholesale investor to invest in their existing hedge funds. I might qualify next year, but investing via the stock exchange would be a lot less hassle assuming I could get in at a reasonable price.
The Hearts and Minds LIC started trading today and is trading above the IPO price. I topped up the allocation that I got in the IPO to the number of shares I originally wanted to invest in. I don't classify this as a hedge fund, as they are not planning to take short positions and there are no performance fees. Actually, there are no management fees. Instead 1.5% of NAV will be donated to charity each year.
The Hearts and Minds LIC started trading today and is trading above the IPO price. I topped up the allocation that I got in the IPO to the number of shares I originally wanted to invest in. I don't classify this as a hedge fund, as they are not planning to take short positions and there are no performance fees. Actually, there are no management fees. Instead 1.5% of NAV will be donated to charity each year.
Sunday, November 11, 2018
Got Online Access to My US Bank Account
I couldn't get online access to my account at Keybank because they required a US phone number as a security measure. This meant I also couldn't transfer money between Keybank and Interactive Brokers. So, I now bought a US phone number through Skype! I now have access to my account (my old password and username from First Niagara still work, and I managed to initiate a transfer of money to Interactive Brokers. Have to wait and see if it really works, though.
Saturday, November 10, 2018
Private Equity and Venture Capital Indices
I commented that I didn't have a good proxy for private equity and venture capital. So, I went and found one and came up with these indices from DSC Quantitative Group. What they do is regress a quarterly indices of private equity buyout and venture capital funds from Thomson Reuters on various sector indices of listed stocks. They update these weights each time Thomson Reuters produce a new number. Because they are using listed stock indices as proxies they can then produce a daily index for private equity. The fit of the proxy to the underlying index is not too bad. This is for venture capital:
The biggest deviation is during the financial crisis - unlisted private equity fell by more than the proxy index had predicted. When we compare the proxy to the NASDAQ total return index, it looks superficially like a leveraged version of the index:
When I regress it on monthly NASDAQ total return index data for 2008 to 2018, I get a beta of 1.15 and annual alpha of 6%. This suggests that venture capitalists add value by rotating the sectors that they invest in over time and it's not just about leverage:
Alpha is given by the intercept of 0.4% per month. I didn't do the proper CAPM regression where you are supposed to deduct risk free returns from the two returns series first. Given the volatility here and low risk free rates since 2008, I doubt it would make much difference.
Interestingly, the Cambridge VC index estimates much lower returns, close to the returns of the NASDAQ index itself.
You could do all this analysis for the buyout private equity index too. You'd want to regress that on the S&P 500 total return index instead.
The biggest deviation is during the financial crisis - unlisted private equity fell by more than the proxy index had predicted. When we compare the proxy to the NASDAQ total return index, it looks superficially like a leveraged version of the index:
When I regress it on monthly NASDAQ total return index data for 2008 to 2018, I get a beta of 1.15 and annual alpha of 6%. This suggests that venture capitalists add value by rotating the sectors that they invest in over time and it's not just about leverage:
Alpha is given by the intercept of 0.4% per month. I didn't do the proper CAPM regression where you are supposed to deduct risk free returns from the two returns series first. Given the volatility here and low risk free rates since 2008, I doubt it would make much difference.
Interestingly, the Cambridge VC index estimates much lower returns, close to the returns of the NASDAQ index itself.
You could do all this analysis for the buyout private equity index too. You'd want to regress that on the S&P 500 total return index instead.
Thursday, November 08, 2018
Target Portfoilo Performance
In October the target portfolio lost 2.83% in Australian Dollar terms. In USD terms the model portfolio lost 3.43%. This model portfolio doesn't include a proxy for private equity, as I don't know a good one. The ASX lost 6.04%. It was hard not to lose money last month. In the last 10 years the model portfolio returned 8.63% p.a. vs. 11.54% including franking credits for the ASX. In the longer term though the target portfolio ("composite") has about matched the returns on Australian shares with lower volatility:
So it's not that necessary to leverage the portfolio to get good returns. The chart shows returns in Australian Dollar terms though bond and real estate are US dollar returns to two TIAA funds invested in those sectors.
So it's not that necessary to leverage the portfolio to get good returns. The chart shows returns in Australian Dollar terms though bond and real estate are US dollar returns to two TIAA funds invested in those sectors.
Wednesday, November 07, 2018
Model Performed Badly Since I Stopped Trading
Since I decided to temporarily stop trading the model has performed badly losing about 9% while the NASDAQ 100 index is down about 4%. It still gained 5% for October overall while the index was down 8.7%. I gained 18% on capital invested due to leverage. It's good I stopped trading when I did.
Saturday, November 03, 2018
October 2018 Report
As I'm sure you know, this month was very volatile, which is good for trading but not for the performance of investments generally. This was a good test of our overall strategy, except that I abandoned trading after 17 October when I found the model was overfitted (and I also got ill with flu/pneumonia or something for the rest of the month). At the end of the month we received the grant of probate and so I am now adding in the inherited assets (cash and half an apartment) from the end of this month. This will suppress returns on both the upside and downside in the near future but doesn't affect the numbers for this month.
The Australian Dollar fell from USD 0.7228 to USD 0.7083. The MSCI World Index fell 7.47% and the S&P 500 fell 6.84%. The ASX 200 fell 6.04%. All these are total returns including dividends. We lost 5.30% in Australian Dollar terms and 7.20% in US Dollar terms. So, we outperformed both Australian and international markets.
Because of the high volatility this month here is a detailed report on the performance of all investments and asset classes:
The table also shows the shares of these investments in our post-inheritance portfolio. Futures contracts are at the bottom. It doesn't make sense to compute shares or rates of return for those. Yeas, we lost a total of AUD 117k, which is our worst ever monthly result in absolute dollars. Things that worked quite well in this market crash:
The following is table of investment performance statistics computed over the last 60 months (extended from 36 months previously) of data:
The first two rows gives the annual rate of return and Sharpe ratio for our investment performance in US dollars and Australian dollars. The other statistics are in comparison to the two indices. Based on beta, compared to the MSCI World Index we seem to be slightly geared, while compared to the Australian index we are less sensitive to market movements. We have a positive alpha compared to the Australian and a negative alpha compared to world markets. We capture more of the up movements and less of the down movements in the Australian market and the reverse in the international markets. The fall in the Australian Dollar over this period explains the poor performance compared to international benchmarks. The rate of return in USD terms is just horrible. US markets have been super strong over this period compared to the rest of the world.
We actually moved away from the new long-run asset allocation in quite a dramatic way with the infusion of cash:
Total leverage includes borrowing inside leveraged (geared) mutual (managed) funds. The allocation is according to total assets including the true exposure in leveraged funds. All asset classes apart from cash and real estate fell as I added the inherited assets. My share of the inherited apartment is about 6% of net worth. Australian large cap fell by more as I switched out of the CFS Geared Share Fund just before the market correction got going. Hedge funds were boosted by the addition of Tribeca (TGF.AX), which started trading on the ASX and Pershing Square Holdings, which I made a new investment in.
We also invest AUD 2k monthly in a set of managed funds, and there are also retirement contributions. Then there are distributions from funds and dividends.
The Australian Dollar fell from USD 0.7228 to USD 0.7083. The MSCI World Index fell 7.47% and the S&P 500 fell 6.84%. The ASX 200 fell 6.04%. All these are total returns including dividends. We lost 5.30% in Australian Dollar terms and 7.20% in US Dollar terms. So, we outperformed both Australian and international markets.
Because of the high volatility this month here is a detailed report on the performance of all investments and asset classes:
The table also shows the shares of these investments in our post-inheritance portfolio. Futures contracts are at the bottom. It doesn't make sense to compute shares or rates of return for those. Yeas, we lost a total of AUD 117k, which is our worst ever monthly result in absolute dollars. Things that worked quite well in this market crash:
- PSSAP Superannuation fund - this fell very little, by contrast with Unisuper, which surprised me.
- International hedge funds: Platinum, Tribeca, and Pershing, each did fairly well in relative terms. We should invest fully in these (12.5% is allocated to them in the model portfolio and 10% to Australian hedge funds).
- Futures: Our own futures trading worked perfectly until I stopped and Winton's downside was not too bad (better than in February), but still not performing with zero or negative correlation to equity markets. Gold rose (will be a priority to invest in it). We need to get trading working, but it will take me a lot of time to do the needed research.
- Real estate, CFS Diversified Fund etc all had more limited downside as we'd expect (estimated return for CFS Conservative Fund was negatively affected by trading).
- Cadence Capital, which fits in the (mostly) Australian hedge fund category, fell sharply.
- China Fund - this isn't surprising given the supposed drivers of the market correction.
- Yellow Brick Road - I should have sold out of this when the Mercantile offer terminated
The following is table of investment performance statistics computed over the last 60 months (extended from 36 months previously) of data:
This month I made USD 6k trading futures. This is the second best result to date and occurred as the NDX declined for the month. As I stopped trading partway through the month, I won't post the usual comparison of market, model, and my own performance. There seems to be potential here, but we need a system that is robust to different market conditions.
We actually moved away from the new long-run asset allocation in quite a dramatic way with the infusion of cash:
We also invest AUD 2k monthly in a set of managed funds, and there are also retirement contributions. Then there are distributions from funds and dividends.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)